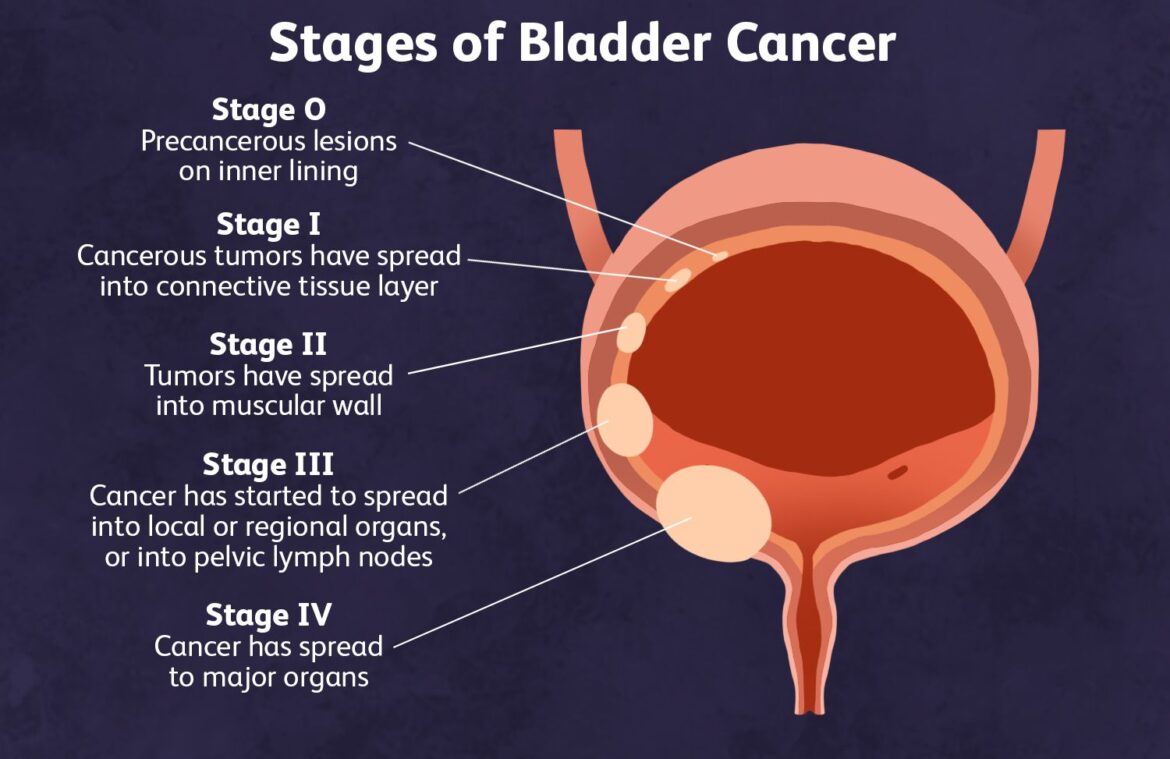
Urinary Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the bladder lining. Early detection and treatment are crucial for a good prognosis.
Symptoms
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Frequent urination
- Painful urination
- Pelvic pain
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves urine tests, cystoscopy, and imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs. A biopsy may be performed to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Treatment Options
- Surgery: Ranges from transurethral resection (TURBT) to remove tumors to cystectomy, where part or all of the bladder is removed.
- Chemotherapy: Used before surgery to shrink tumors or after to kill remaining cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Targets cancer cells with high-energy beams.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Post-Treatment Care Regular follow-ups, imaging tests, and lifestyle changes are crucial to monitor for recurrence and maintain health.










