Urinary Tract Infection in Female
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
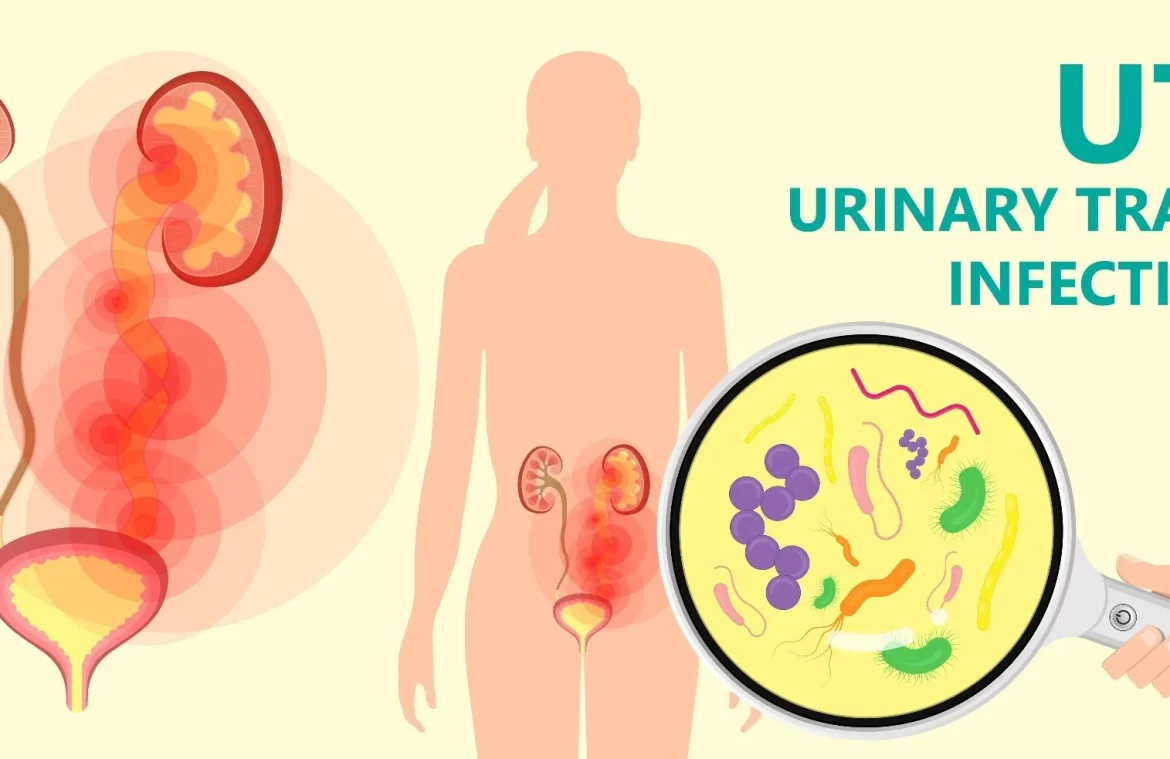
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are common infections that affect the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys. Women are particularly prone to UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria easier access to the bladder.
Symptoms of UTIs
Common symptoms of UTIs in women include:
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation during urination
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain, particularly in the center of the pelvis and around the area of the pubic bone
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Fever and chills (if the infection has reached the kidneys)
Causes of UTIs
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract through the urethra and multiplying in the bladder. The most common bacteria responsible for UTIs is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is typically found in the gastrointestinal tract. Other factors that can contribute to UTIs include:
- Sexual activity
- Certain types of birth control (such as diaphragms and spermicidal agents)
- Menopause
- Urinary tract abnormalities
- Blockages in the urinary tract (such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate)
- A suppressed immune system
- Catheter use
Diagnosis of UTIs
Diagnosing a UTI typically involves:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Discussing symptoms and medical history.
- Urine Sample Analysis: Testing a urine sample for bacteria, white blood cells, and red blood cells.
- Urine Culture: Growing bacteria from the urine sample in a lab to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective treatment.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be needed to check for abnormalities in the urinary tract.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure in which a thin tube with a camera (cystoscope) is inserted into the urethra to view the bladder.
Treatment Options for UTIs
UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics. The type of antibiotic and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria found in the urine. Common treatments include:
- Antibiotics: The most commonly prescribed antibiotics include trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, cephalexin, and ceftriaxone.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter medications like phenazopyridine can help relieve discomfort.
Preventing UTIs
Preventing UTIs involves several lifestyle changes and habits, including:
- Drinking plenty of water to dilute urine and help flush out bacteria.
- Urinating frequently and fully emptying the bladder.
- Wiping from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria from the anal region from spreading to the urethra.
- Avoiding irritating feminine products, such as deodorant sprays, douches, and powders, which can irritate the urethra.
- Urinating immediately after sexual intercourse to help flush out bacteria.
- Changing birth control methods if diaphragms or spermicides are contributing to frequent infections.
Why Choose Us?
- Expert Care: Dr. Santosh Agrawal specializes in diagnosing and treating UTIs, offering expert care tailored to each patient.
- Comprehensive Approach: We provide thorough evaluations and personalized treatment plans to effectively manage and prevent UTIs.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Our clinic is equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic tools to accurately identify the cause of infections.
- Patient Education: We emphasize patient education, empowering women with the knowledge and tools to prevent future UTIs.
If you are experiencing symptoms of a UTI, don’t hesitate to contact us to schedule an appointment. Early treatment is crucial to prevent complications and ensure your well-being.










